Difference between revisions of "Idrija Mine Museum"
| (41 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Article | {{Article | ||
| − | | status = | + | | status = |
| maintainer = Ivan Pirnat | | maintainer = Ivan Pirnat | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| street = Bazoviška 2 | | street = Bazoviška 2 | ||
| town = SI-5280 Idrija | | town = SI-5280 Idrija | ||
| + | | map = https://www.openstreetmap.org/?lon=14.0227&lat=45.99965&zoom=17&layer=mapnik | ||
| telephone = 386 (0) 5 374 3920 | | telephone = 386 (0) 5 374 3920 | ||
| fax = 386 (0) 5 374 3934 | | fax = 386 (0) 5 374 3934 | ||
| − | | email = | + | | email = info@cudhg-idrija.si |
| − | | website = http://www. | + | | website = http://www.cudhg-idrija.si/ |
| − | | founded by = | + | | founded by = |
| organised by = | | organised by = | ||
| − | | managed by = | + | | managed by = Idrija Mercury Heritage Management Centre |
| published by = | | published by = | ||
| + | | opening hours = 10am and 3pm Mon-Fri; 10am, 3pm and 4pm Sat-Sun and holidays | ||
| contacts = | | contacts = | ||
{{Contact | {{Contact | ||
| − | | name = | + | | name = Tatjana Dizdarević |
| − | | role = Director | + | | role = Acting Director |
| street = | | street = | ||
| town = | | town = | ||
| website = | | website = | ||
| − | | email = | + | | email = |
| − | | telephone = 386 | + | | telephone = |
| + | | fax = | ||
| + | }}{{Contact | ||
| + | | name = Visit | ||
| + | | role = Antonijev rov, entrance | ||
| + | | street = Kosovelova 3 | ||
| + | | town = SI-5280 Idrija | ||
| + | | website = | ||
| + | | email = | ||
| + | | telephone = 386 (0) 5 377 1142 | ||
| fax = | | fax = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | | accounts = | ||
| + | https://www.facebook.com/RudnikZivegaSrebraIdrija/ | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Teaser| | {{Teaser| | ||
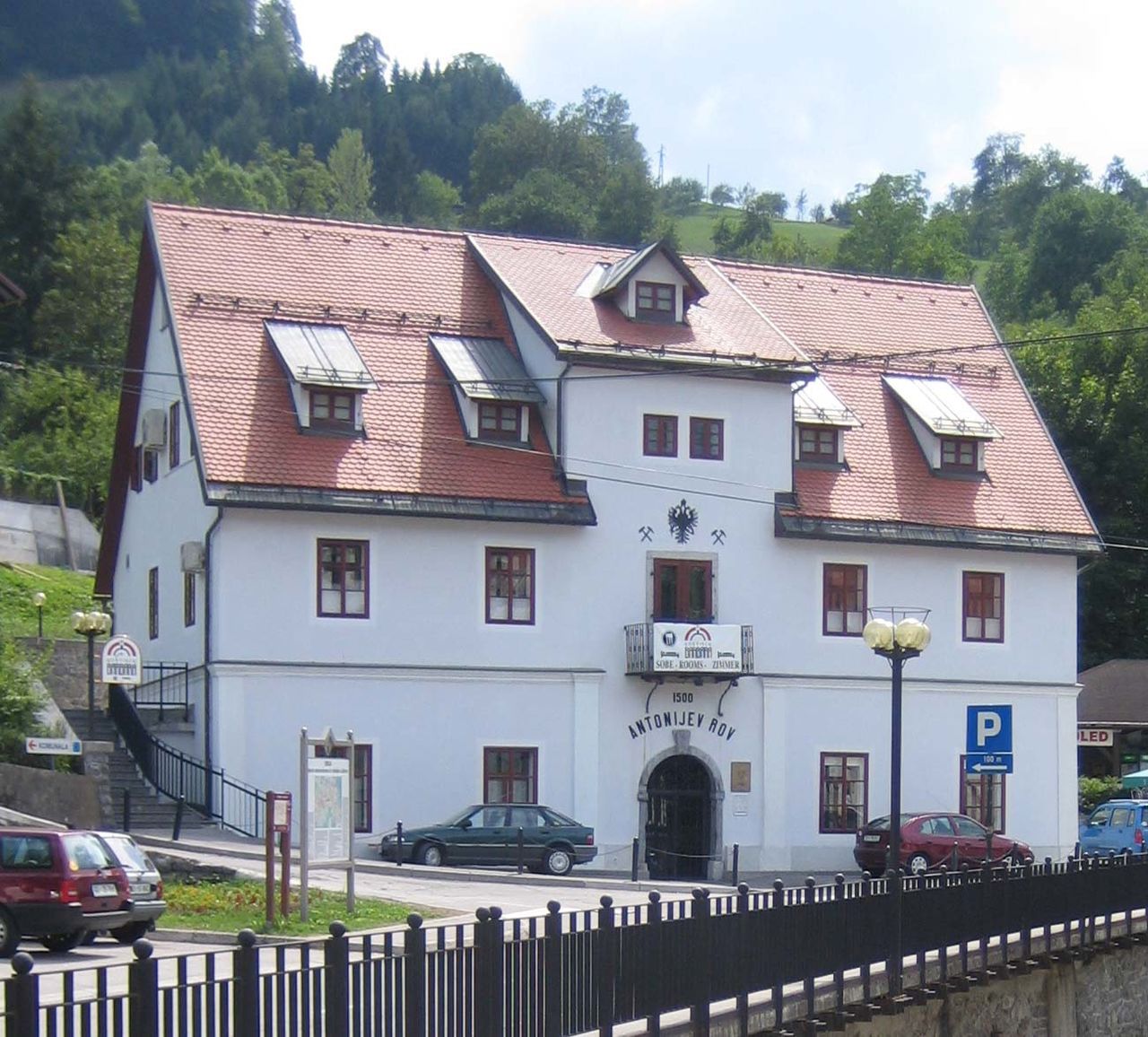
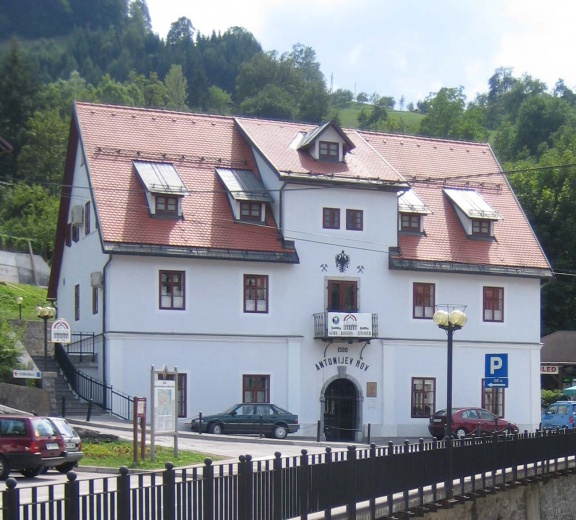
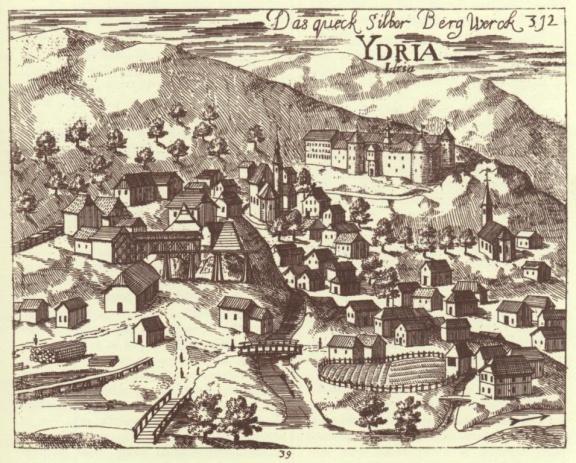
| − | + | Thanks to having the second largest mercury mine in the world the town of [[Municipality of Idrija|Idrija]] was for centuries considered to be the centre of scientific and technological progress in the region. The administration of the Idrija Mercury Mine was housed in the [[Gewerkenegg Castle]] (16th century) which dominates the town. Today it houses the [[Idrija Municipal Museum]], which together with the [[Idrija Mine Museum]] takes care of the region's rich technical, geological, technological, ethnological, and cultural heritage. The Idrija Mine Museum is managed by THE Idrija Mercury Heritage Management Centre. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In 2012 the ''Heritage of Mercury. Almadén and Idrija'' project was submitted to UNESCO and both cities entered its [[:Category:UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Slovenia|World Heritage List]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | {{Image|Idrija Mine Museum 2006 entrance.jpg}} | ||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Mercury mining in Idrija== | ||
| + | The history of mining in Idrija dates back to 1490. Only the Almadén mercury mine in Spain was bigger and dates back to the Roman times. Both towns were so famous that their names were used in North America for the mining towns of New Idria and New Almadén. Until World War I the Idrija Mercury Mine was one of the best technically equipped mines in Europe. By burning cinnabar ore, the mercury miners of Idrija mined over 13 per cent of the world production of this ore. In 500 years Idrija exported 107,700 tons of this liquid metal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1986 the decision was made to close the mine for commercial, geological, and ecological reasons. It finally closed in 1995 but some of its shafts and facilities have remained open for tourists. Today the company's main task is to close down the mine and to manage the consequences of 500 year mining, that is to secure the shafts and to monitor the pollution of the environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==UNESCO World Heritage List== | ||
| + | The [[:Category:Mercury mining heritage|mercury mining heritage in Idrija]] (together with the oldest theatre house in Slovenia, the warehouse, the city hall, the old town square, the science secondary school, the [[Gewerkenegg Castle]], etc.) was successfully nominated to become a [[UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Slovenia|UNESCO world heritage protected site]] in 2012. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first project for the candidature was prepared in 2007 under the title ''Idrija on the Mercury Route of the Intercontinental Camino Real'' together with Almadén (Spain) and San Luis Potosí (Mexico). The development of the "Mercury Route" as part of the Intercontinental Camino Real was greatly influenced by the 1554 discovery of amalgamation in America. The process used mercury in acquiring silver and gold from ore and sparked a major increase in the demand for mercury (Idrija, Almadén). The metal was foremost exported to Mexico where it was used in silver mines. This discovery influenced the global development of manufacture, technology, and trade in mercury as well as facilitated an intensive transfer of technological knowledge and changes in the global economy, social relations, science, and culture. | ||
== Museum sites == | == Museum sites == | ||
| − | Idrija mine ore deposit is unique. Quoting | + | The Idrija mine ore deposit is unique on the world. Quoting a Soviet geologist Vladimir Ivanovich Smirnov (1910–1988): "I have seen many ore deposits in different parts of the world and some of them quite complex. But I openly admit that such a complex geological structure as in Idrija, I haven't yet seen. Without any doubt this is structurally one of the most complex endogenous ore deposits in the world." The Mine Museum has a rich '''geological collection''' with more than 800 different samples of ore and mineral from Idrija mercury ore deposit on display at the [[Idrija Municipal Museum]]. |
| − | Mine Museum has rich '''geological collection''' with more than 800 different samples of ore and mineral from Idrija mercury ore deposit on display | ||
| − | + | '''Anthony's Shaft''' is the oldest part of the mine, today also one of the oldest preserved mine entrances in Europe. Named after Anthony of Padua, a patron saint of miners and protector from mine accidents, the shaft was dug back in 1500, soon after mercury was first discovered. The museum tour is 1,300 metres long in an authentically preserved mine. It starts in the 18th-century Šelštev House where miners used to take the equipment early in the morning before entering the mine. Here visitors to the mine watch a multivision show in the former call-in room, than professional guides take them through shafts and illuminated galleries with life-size mannequins which illustrate the various mining jobs to the unique underground Chapel of the Holy Trinity, dating from the mid-18th century, the time of the greatest prosperity for the Idrija mine. The shaft was opened for the public in 1994. At the entrance, visitors are given raincoats to wear during the tour and are greeted with the typical miner's greeting ''srečno'' ("good luck"), which gets its true meaning when entering the shaft. | |
| − | [[Francis's Shaft]] was sinked | + | '''[[Francis's Shaft]]''' was sinked 1792 and is named after the Roman-German Emperor Franz Joseph the Second (1792–1806). It is a big transport shaft with the only preserved huge exporting machine Siemens-Stuckert, still in operating condition. Francis's Shaft has the largest preserved steam piston machine in Slovenia and probably in Europe. This Kley's water pump was made in 1893 in the Škoda-Pilsen Factory and operated until 1948. Francis's Shaft is administered by the [[Idrija Municipal Museum]]. |
| − | '''Joseph Shaft''' | + | Sinked in 1786, '''Joseph Shaft''' is 420 meters deep and connects all 15 levels of the mine. It was closed in year 2007 and consists of a tower, an exporting machine with big driving mechanisms, a loading station of transport cable, a blacksmith workshop, and dressing rooms for miners. It is now closed for the public. |
| − | '''Ore Foundry''' of the | + | The '''Ore Foundry''' was the part of the Idrija Mercury Mine that was still in operation until 1995. Over 500 years smelting of ore was developed from a simple charcoal heap to today's rotating furnaces. The Čermak-Špirekova furnace, technical heritage made from 1873 to 1886, operated until 1974. The foundry consists of transport cable, a separation area, a transport belt, a reservoir, and a smoke chamber with special chimney pipes. The plan is to revitalise this part of the Idrija Mercury Mine. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The whole Idrijan region is in the process of becoming a "Geopark" with unique natural and cultural features based on a principle of sustainable development, embedded in the European Geopark Network under UNESCO's Division of Ecological and Earth Sciences patronage. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[:Category:Mercury mining heritage|Mercury mining heritage on Culture.si]] | ||
* [[Idrija Municipal Museum]] | * [[Idrija Municipal Museum]] | ||
* [[Miner's House - Ethnological Collection]] | * [[Miner's House - Ethnological Collection]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 82: | ||
* [[Flood Dams, Klavže]] | * [[Flood Dams, Klavže]] | ||
* [[Francis's Shaft]] | * [[Francis's Shaft]] | ||
| + | * [[Municipality of Idrija]] | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | |||
* [http://www.muzej-idrija-cerkno.si Idrija Municipal Museum website] | * [http://www.muzej-idrija-cerkno.si Idrija Municipal Museum website] | ||
* [http://www.idrija-turizem.si/en/1.nivo/heritage-of-city-idrija.html Idrija Heritage] | * [http://www.idrija-turizem.si/en/1.nivo/heritage-of-city-idrija.html Idrija Heritage] | ||
| − | * [http://www. | + | * [https://www.norwaygrants.si/en/news/town-idrija-proudly-unveils-restored-monument-heritage-mercury-dedicated-generations-idrija-miners/ The Norway Grants for restoration of the smelting plant in Idrija] |
| − | * [http:// | + | |
| − | * [http://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5154/ Idrija on the Mercury Route of the Intercontinental Camino Real, UNESCO tentative list (2007 | + | UNESCO World Heritage List |
| + | *[http://www.cudhg-idrija.si/en/ Mercury Mine Idrija website] | ||
| + | *[http://www.mizks.gov.si/fileadmin/mizks.gov.si/pageuploads/novice/pdf/SPAIN_Slovenia_AB_evaluation_Almaden_Idrija_2012.pdf Heritage of Mercury. Almadén and Idrija (Spain, Slovenia)] (pdf) | ||
| + | * [http://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5154/ Idrija on the Mercury Route of the Intercontinental Camino Real, UNESCO tentative list (Spain, Mexico, Slovenia)], the abandoned candidature from 2007 | ||
| + | Further reading | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Almad%C3%A9n Almadén on Wikipedia] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mercury_%28element%29 Mercury on Wikipedia] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mercury_%28element%29 Mercury on Wikipedia] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{gallery}} | ||
[[Category:Monuments and sites]] | [[Category:Monuments and sites]] | ||
| Line 73: | Line 103: | ||
[[Category:Industrial and technical heritage]] | [[Category:Industrial and technical heritage]] | ||
[[Category:Mercury mining heritage]] | [[Category:Mercury mining heritage]] | ||
| + | [[Category:UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Slovenia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:01, 10 November 2019
Mercury mining in Idrija
The history of mining in Idrija dates back to 1490. Only the Almadén mercury mine in Spain was bigger and dates back to the Roman times. Both towns were so famous that their names were used in North America for the mining towns of New Idria and New Almadén. Until World War I the Idrija Mercury Mine was one of the best technically equipped mines in Europe. By burning cinnabar ore, the mercury miners of Idrija mined over 13 per cent of the world production of this ore. In 500 years Idrija exported 107,700 tons of this liquid metal.
In 1986 the decision was made to close the mine for commercial, geological, and ecological reasons. It finally closed in 1995 but some of its shafts and facilities have remained open for tourists. Today the company's main task is to close down the mine and to manage the consequences of 500 year mining, that is to secure the shafts and to monitor the pollution of the environment.
UNESCO World Heritage List
The mercury mining heritage in Idrija (together with the oldest theatre house in Slovenia, the warehouse, the city hall, the old town square, the science secondary school, the Gewerkenegg Castle, etc.) was successfully nominated to become a UNESCO world heritage protected site in 2012.
The first project for the candidature was prepared in 2007 under the title Idrija on the Mercury Route of the Intercontinental Camino Real together with Almadén (Spain) and San Luis Potosí (Mexico). The development of the "Mercury Route" as part of the Intercontinental Camino Real was greatly influenced by the 1554 discovery of amalgamation in America. The process used mercury in acquiring silver and gold from ore and sparked a major increase in the demand for mercury (Idrija, Almadén). The metal was foremost exported to Mexico where it was used in silver mines. This discovery influenced the global development of manufacture, technology, and trade in mercury as well as facilitated an intensive transfer of technological knowledge and changes in the global economy, social relations, science, and culture.
Museum sites
The Idrija mine ore deposit is unique on the world. Quoting a Soviet geologist Vladimir Ivanovich Smirnov (1910–1988): "I have seen many ore deposits in different parts of the world and some of them quite complex. But I openly admit that such a complex geological structure as in Idrija, I haven't yet seen. Without any doubt this is structurally one of the most complex endogenous ore deposits in the world." The Mine Museum has a rich geological collection with more than 800 different samples of ore and mineral from Idrija mercury ore deposit on display at the Idrija Municipal Museum.
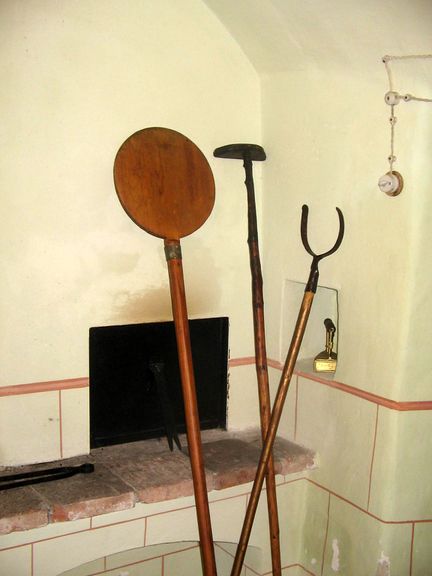
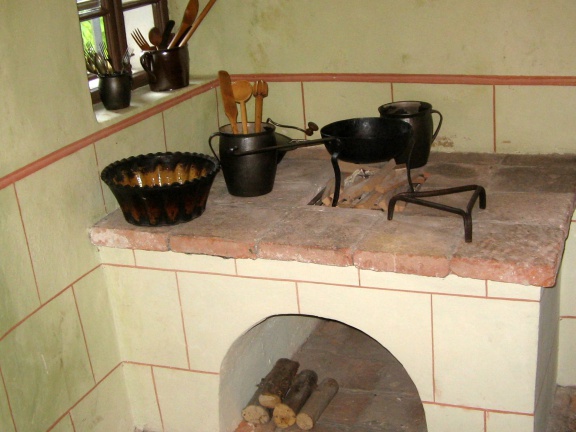
Anthony's Shaft is the oldest part of the mine, today also one of the oldest preserved mine entrances in Europe. Named after Anthony of Padua, a patron saint of miners and protector from mine accidents, the shaft was dug back in 1500, soon after mercury was first discovered. The museum tour is 1,300 metres long in an authentically preserved mine. It starts in the 18th-century Šelštev House where miners used to take the equipment early in the morning before entering the mine. Here visitors to the mine watch a multivision show in the former call-in room, than professional guides take them through shafts and illuminated galleries with life-size mannequins which illustrate the various mining jobs to the unique underground Chapel of the Holy Trinity, dating from the mid-18th century, the time of the greatest prosperity for the Idrija mine. The shaft was opened for the public in 1994. At the entrance, visitors are given raincoats to wear during the tour and are greeted with the typical miner's greeting srečno ("good luck"), which gets its true meaning when entering the shaft.
Francis's Shaft was sinked 1792 and is named after the Roman-German Emperor Franz Joseph the Second (1792–1806). It is a big transport shaft with the only preserved huge exporting machine Siemens-Stuckert, still in operating condition. Francis's Shaft has the largest preserved steam piston machine in Slovenia and probably in Europe. This Kley's water pump was made in 1893 in the Škoda-Pilsen Factory and operated until 1948. Francis's Shaft is administered by the Idrija Municipal Museum.
Sinked in 1786, Joseph Shaft is 420 meters deep and connects all 15 levels of the mine. It was closed in year 2007 and consists of a tower, an exporting machine with big driving mechanisms, a loading station of transport cable, a blacksmith workshop, and dressing rooms for miners. It is now closed for the public.
The Ore Foundry was the part of the Idrija Mercury Mine that was still in operation until 1995. Over 500 years smelting of ore was developed from a simple charcoal heap to today's rotating furnaces. The Čermak-Špirekova furnace, technical heritage made from 1873 to 1886, operated until 1974. The foundry consists of transport cable, a separation area, a transport belt, a reservoir, and a smoke chamber with special chimney pipes. The plan is to revitalise this part of the Idrija Mercury Mine.
The whole Idrijan region is in the process of becoming a "Geopark" with unique natural and cultural features based on a principle of sustainable development, embedded in the European Geopark Network under UNESCO's Division of Ecological and Earth Sciences patronage.
See also
- Mercury mining heritage on Culture.si
- Idrija Municipal Museum
- Miner's House - Ethnological Collection
- Idrija Kamšt
- Flood Dams, Klavže
- Francis's Shaft
- Municipality of Idrija
External links
- Idrija Municipal Museum website
- Idrija Heritage
- The Norway Grants for restoration of the smelting plant in Idrija
UNESCO World Heritage List
- Mercury Mine Idrija website
- Heritage of Mercury. Almadén and Idrija (Spain, Slovenia) (pdf)
- Idrija on the Mercury Route of the Intercontinental Camino Real, UNESCO tentative list (Spain, Mexico, Slovenia), the abandoned candidature from 2007
Further reading